Up to 24 cash back Active Transport. One of the basic examples of cellular activity which uses energy released by ATP is the movement of muscles.

Difference Between Mendelian And Non Mendelian Inheritance Comparison Summary Science Biology Mendelian Inheritance Biology Lessons
It usually uses energy from ATP to drive transport primary active transport but it can also be powered by an established electrochemical gradient secondary active transport.

. Chapter 14 and 15 pp 140-143 and pp 146-151 Overview. In active transport carrier proteins which are located at membrane use energy in the form of ATP to transport molecules against concentration gradient of cell membrane. In secondary active transport it uses energy stored in the concentration gradients of ions.
It requires energy in the form of ATP. Give and explain three examples of primary active transport. Describe an instance of active transport of protons H during the light reactions and explain the source of energy for this instance of active transport.
The membrane proteins which help in the. Some pumps which carry out primary active transport couple directly with ATP to drive their action. Secondary active transport however makes use of potential energy which is usually derived through exploitation of an electrochemical gradient.
Describe what the proton motive force is and explain. ATP is hydrolyzed by transport proteins releasing energy. In primary active transport the carrier protein uses energy directly from ATP through hydrolysis.
Active transport is most commonly accomplished by a transport protein that undergoes a change in shape when it binds with the cells fuel a molecule called adenosine triphosphate ATP. Active transport of small molecular-size material uses integral proteins in the cell membrane to move the materialthese proteins are analogous to pumps. ACTIVE TRANSPORT AND GLUCOSE TRANSPORT.
It is a selective process as certain molecules can only be transported by certain proteins. Three sodium ions form inside the cell bind to the pump. The muscle cells use ATP mainly for two things that is for active.
Active transport is the movement of particles against a concentration gradient from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration at a rate faster than diffusion. A primary active transport b secondary active transport c facilitated diffusion d passive diffusion e osmosis Answer. Describe an instance of facilitated diffusion of protons H during the light reactions and explain why this instance of facilitated diffusion does not require energy.
17 In this transport process the energy from hydrolysis of ATP is used to drive substances across the membrane against their own concentration gradients. Most ion pumps of interest to us are transport ATPases that is they are bifunctional molecules that. These proteins are very specific to certain substances and are sensitive to.
Electrons are transferred down the electron transport chain. The muscle cells utilize both fatty acids and glucose for their aerobic respiration and these cells are the prime users of ATP generated by aerobic respiration. Up to 24 cash back The pump is powered by a molecule of ATP.
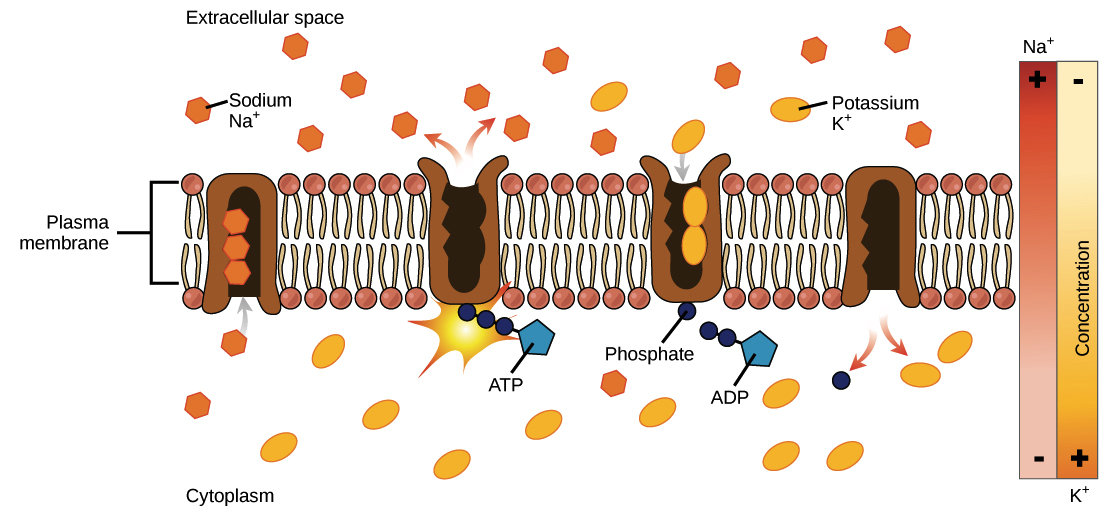
Active Transport Cellular energy is used to to transport substances across the membrane against a concentration gradient Energy is derived from splitting ATP Pumps A transporter protein that uses energy from splitting ATP to change shape and carry a substance across a cellular membrane against its concentration gradient Substances Transported Na K H Ca I- Cl-. Below are the steps that the sodium-potassium pump uses to function. There are three main types of Active Transport.
ATP synthesis utilizes energy obtained from multiple catabolic mechanisms including cellular respiration beta-oxidation and ketosis. In secondary active transport the ATP is not used directly and the energy comes from a gradient that was made by a primary active transport system that just happened to use ATP. Primary active transport occurs in the absence of or against the existing electrochemical gradient and is powered by metabolic energy such as that originated by the exergonic hydrolysis of ATP Fig.
It provides energy to actively transport protons into the space between membranes. Thisenergy is what is used to transport a molecule across a membraneand up its concentration gradient. Active transport is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane in the direction against their concentration gradient ie.
Active Transport is the term used to describe the processes of moving materials through the cell membrane that requires the use of energy. The source of energy. Active transport uses energy stored in ATP to fuel the transport.
Transportation rate reaches maximum when all carrier proteins are being used or are saturated. The Sodium-Potassium pump Exocytosis and Endocytosis. The body is a complex organism and as such it takes energy to maintain proper functioning.
Active transport requires energy to move substances from a low concentration of that substance to a high concentration of that substance in contrast with the process of osmosis. ATP is used in active transport by supplying energy needed to move solutes against a concentration gradient. This is an advantage to living systems because it allows for substances to do work as they move back across the membrane in diffusion and allows proteins to transport in new ways.
In primary active transport the proteins involved are pumps that normally use chemical energy in the form of ATP. 6Ion pumps are the only molecules capable of performing primary active transport. Adenosine triphosphate ATP is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level.
The ATP allows the shape of the pump to change emptying its contents either into or out of the cell. Moving from a low concentration to a high concentration. In primary active transport the ATP is used directly which means that the energy comes from a high-energy phosphate bond being broken.
The protons then diffuse back through the membrane through ATPase. The Phosphate group form a molecule of ATP binds to the pump.

What Role Does Atp Play In The Function Of Active Transport Pumps And Motor Proteins Such As Myosin Kinesin Dynein Quora

Active Transport Movement Of Materials Through A Membrane Against A Concentration Gradient And Requires Energy From The Cell Atp Low Concentration Ppt Video Online Download
0 Comments